



Pathogenic factors of hereditary deafness
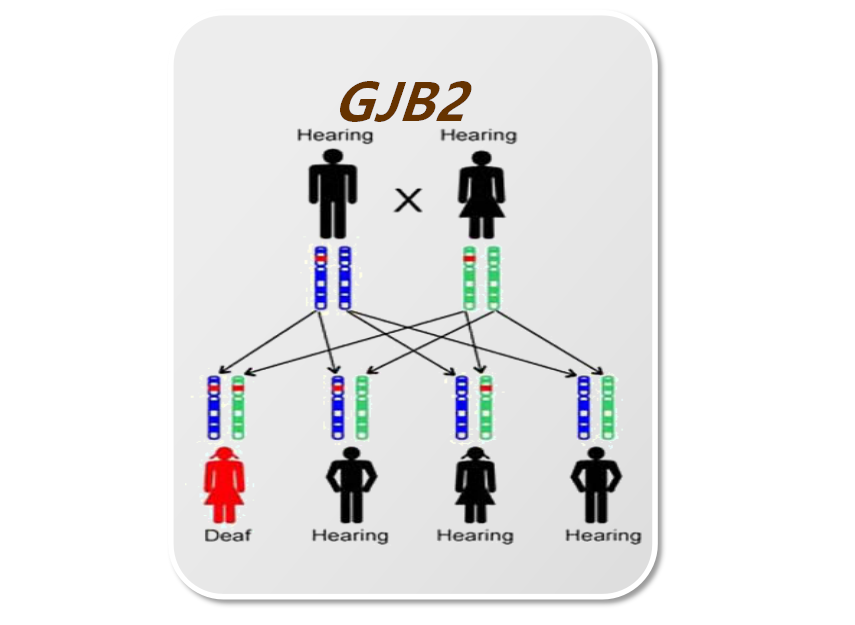
It is the most common defect of the human sensory and acoustic nervous system caused by the genetic material of parents changed and passed on to the offspring. Whether the parents are single or both deaf patients or healthy carriers, deafness genes will be passed on from parents to their children.
| Product name | Related diseases | Gene detection | Detection sites |
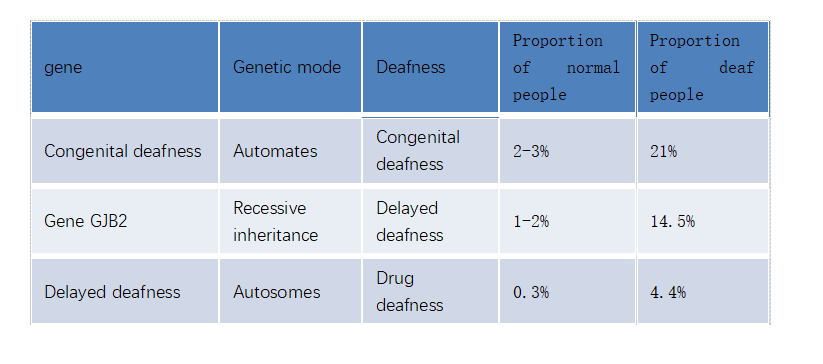
| Congenital ear gene detection kit | Congenital severe sensorineural deafness 2% - 3% of normal people carry the mutant gene |
GJB2 | 235delC 299-300delAT 176del16bp 512insAACG |
| PDS gene mutation detection kit | Large vestibular aqueduct syndrome (LVAS) Congenital or acquired severe sensorineural deafness; 1% - 2% of normal people carry the mutant gene |
Autosomal recessive inheritance | IVS7-2A>G 2168A>G 1229C>T 1174A>T |
| Gene test kit for drug-induced deafness | Drug induced deafness; 3 ‰ normal population carries the mutant gene |
SLC26A4(PDS) | 1555 A>G 1494C>T |
Product advantage
Authoritative and accurate: three types of CFDA registration, 1s013485 certification, S-type amplification curve, 100% consistent with the sequencing results.
Customized screening: the site can be split, prenatal, pregnancy, newborn, hearing-impaired patients and other different groups of targeted testing, more user-friendly.
Comprehensive coverage: 10 loci coverage: hot spot mutations of genes related to congenital otoscopy, delayed otology and drug-induced otodeng.
Simple and fast: the existing fluorescent PCR instrument can detect, with less manual operation, easy to learn and use, high stability, easy to judge, and 1.5 hours to provide the test report.
| Intended for | Target Department | Detection cause | Clinical significance | |
| Premarital examination, pregnancy and childbirth examination | Pre pregnancy couples Maternal Family history of deafness |
Obstetrics and Gynecology Department Premarital examination body Medical examination center |
Most hereditary deafness is recessive; More than 5% of normal people carry the gene of deafness |
Guide scientific breeding; Avoid birth of genetically defective children |
| Newborn hearing screening | Newborn | Obstetrics Department Neonatal department |
Routine hearing screening is easy to miss diagnosis Patients with delayed and drug-induced deafness cannot be detected |
Early diagnosis and early treatment to avoid secondary injury caused by hearing loss |
| Diagnosis and treatment of hearing impairment | Deaf patients and their families Cochlear implant operator |
Department of ENT | Cochlear implant is only effective for neuropathic deafness Most congenital deafness is neural deafness |
Predicting the effect of cochlear implant surgery |
| Medication guidance | Ototoxic drug users | Internal and surgical | Sensitive to aminoglycoside antibiotics in patients with drug-induced deafness | Avoid the tragedy of deafness |